Programmers, system administrators, and power users may need to work at some point with environment variables. Some may want to delete an environment variable; others will want to change its value, and so on. This guide shares how to edit or delete environment variables, as well as how to unset environment variables in Windows:
Contents
- Open the Environment Variables window
- How to edit an environment variable in Windows
- How to edit an environment variable from Command Prompt
- How to edit an environment variable from PowerShell
- How to clear the value of an environment variable in Windows (from Command Prompt)
- How to delete an environment variable in Windows
- How to delete an environment variable from Command Prompt
- How to delete an environment variable from PowerShell
- Why did you want to learn how to edit and delete environment variables in Windows?
Open the Environment Variables window
To make many of the edits shown in this article, you first need to open the Environment Variables window. This guide explains how to do that and shows you the basics about working with environment variables: What are environment variables in Windows?.
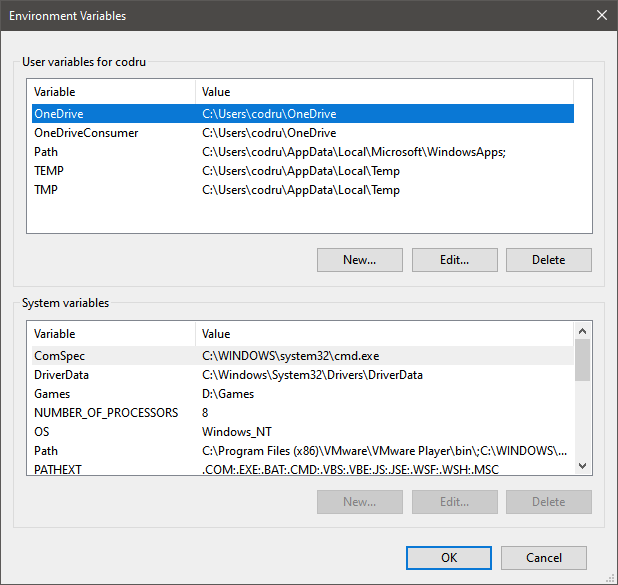
The Environment Variables window in Windows 10
If you want to skip reading it, one path that works the same in all versions of Windows is to open the Run window (Win + R), Command Prompt, or PowerShell and execute the command: rundll32.exe sysdm.cpl,EditEnvironmentVariables.
How to edit an environment variable in Windows
If you want to change the value of an existing environment variable, first select it in the Environment Variables window. Then, click or tap Edit.
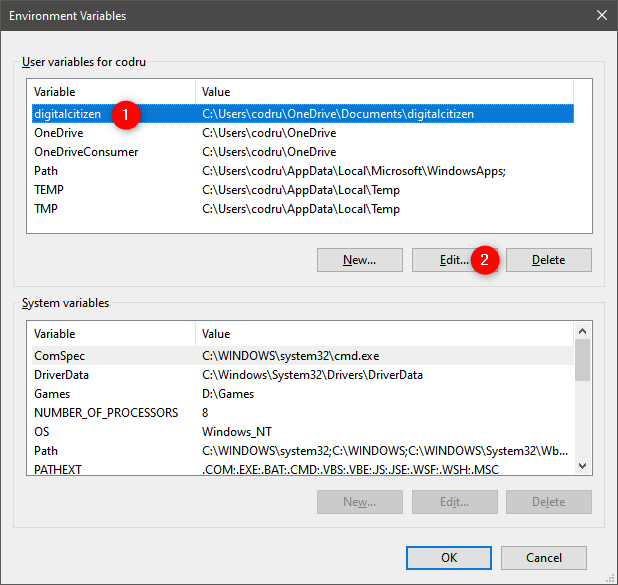
How to edit an environment variable in Windows 10
You are shown a window where you can edit both the name and the value of the variable. Make the modifications you desire and press OK. Then, press OK one more time in the Environment Variables window.
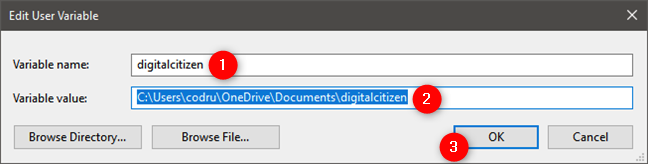
Editing an environment variable
How to edit an environment variable from Command Prompt
You can create a new environment variable, or edit the value of an existing environment variable (but not its name) from the Command Prompt too. The command you have to enter is:
- setx variable_name “value” if you want to create a user environment variable
- setx variable_name “value” /m if you’re going to create a system environment variable
For example, we typed setx TEST “C:\digitalcitizen” and created a user variable named TEST with the value C:\digitalcitizen.
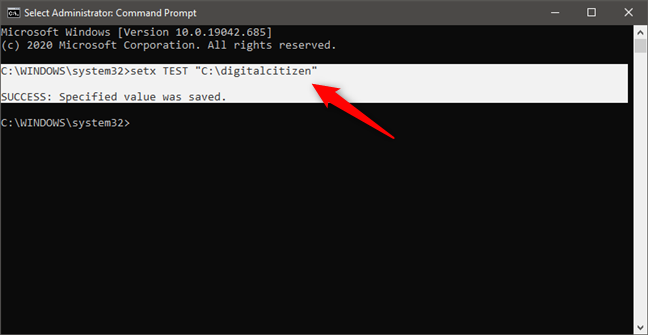
How to set an environment variable using Command Prompt
If we want to change the value of an environment variable, we can run the same setx command but specify a new value for the variable. For instance, executing setx TEST “C:\DC” changes the value of the TEST environment variable to C:\DC.
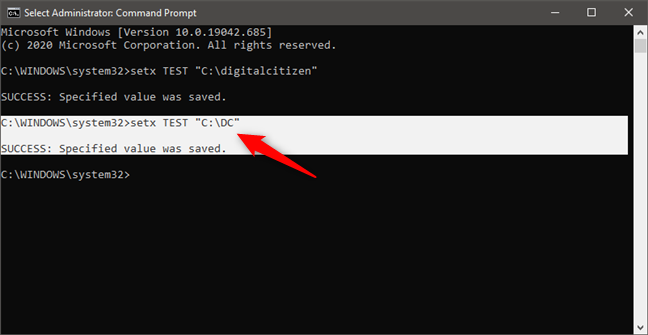
How to change the value of an environment variable in Command Prompt
That works because the setx command rewrites the existing value with the last one you type. Therefore, if you use this command multiple times on the same variable, the variable will keep the last value that you typed.
If you want a variable to have multiple paths in its value, you must write them all, each separated by a semicolon, without spaces, like in the screenshot below.
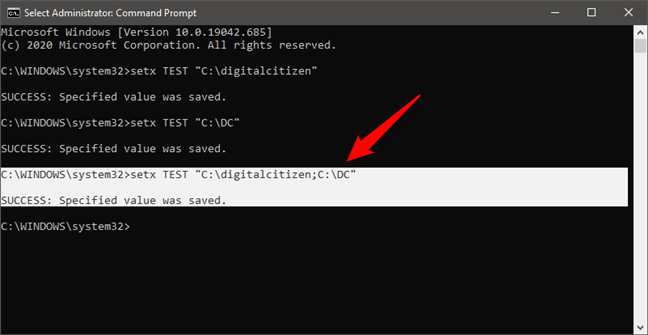
How to add multiple values to an environment variable using Command Prompt
NOTE: You can get a list of all the environment variables available by running the set command in Command Prompt (not setx, and without any parameters). However, if you just created or edited an environment variable, you must close and reopen Command Prompt for the changes to show up.
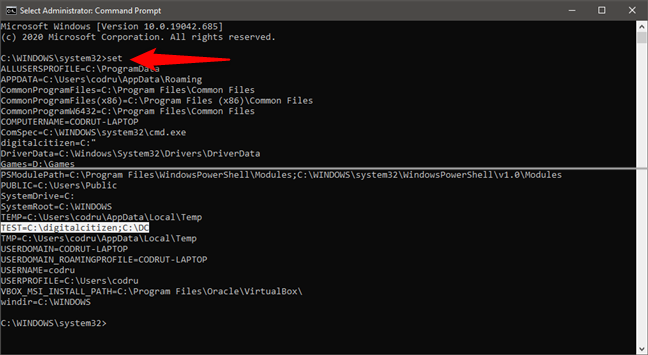
How to see all the environment variables in Command Prompt
How to edit an environment variable from PowerShell
You can also create or edit the value of an existing environment variable from PowerShell. The PowerShell command for that is:
- [Environment]::SetEnvironmentVariable("variable_name","variable_value","User") if you want to create a user environment variable
- [Environment]::SetEnvironmentVariable("variable_name","variable_value","Machine") if you want to create a system environment variable
For instance, we typed [Environment]::SetEnvironmentVariable("TEST","digitalcitizen.life","User") in order to create a user environment variable called TEST with the value digitalcitizen.life. To change the value of the variable later, we can run the same command using a different value. Just like setx in Command Prompt, this command rewrites the value of the specified variable each time you run it.
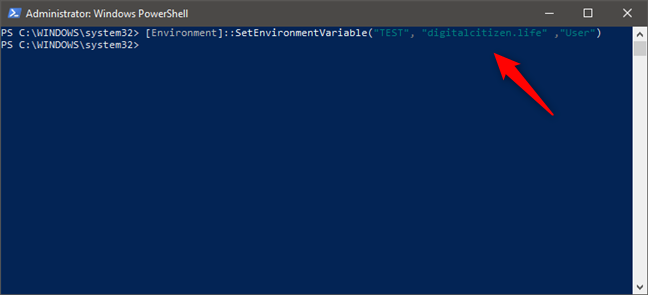
How to set an environment variable with PowerShell
If you want to assign multiple values to a variable, type all of them in the command, with semicolons between each value, as illustrated below.
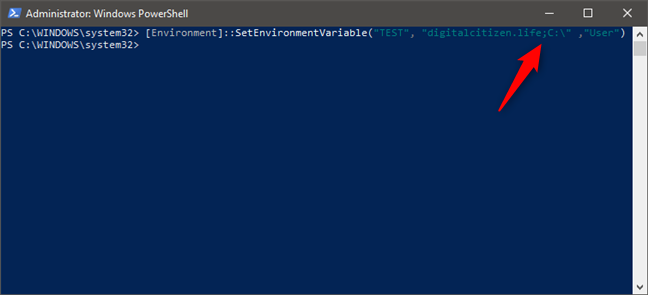
How to add multiple values to an environment variable in PowerShell
NOTE: In PowerShell, you can get a list of all the environment variables by running the Get-ChildItem Env: command. However, if you just created or edited an environment variable, you must close and reopen PowerShell for the changes to show up.
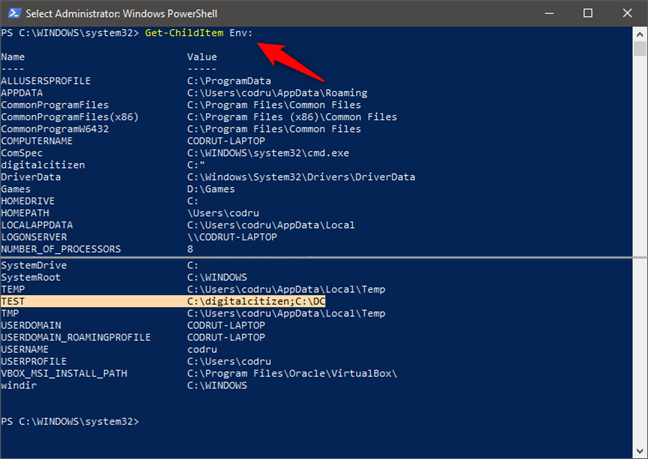
How to see all the environment variables in PowerShell
How to clear the value of an environment variable in Windows (from Command Prompt)
If you want to remove the value of an environment variable (while keeping its name), you cannot do that with the mouse and keyboard from the Environment Variables window. If you select a variable and press Edit, you can delete the value, but you cannot press OK, as this button gets grayed out. Therefore you cannot save your changes.
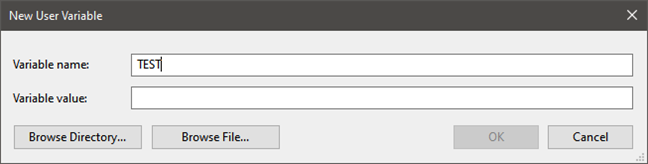
How to clear an environment variable in Windows 10
However, you can clear the value of an environment variable using Command Prompt. To unset an environment variable from Command Prompt, type the command setx variable_name “”. For example, we typed setx TEST “” and this environment variable now had an empty value.
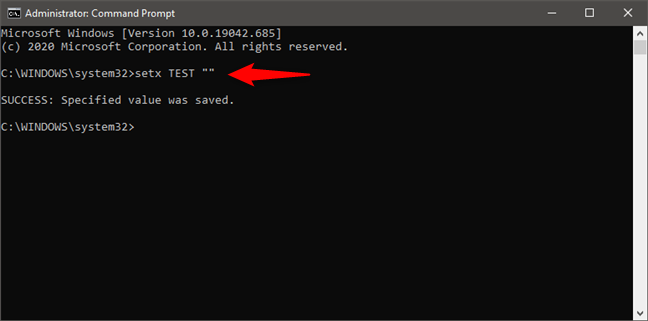
How to clear an environment variable with Command Prompt
Next, let’s see how to remove an environment variable.
How to delete an environment variable in Windows
If you no longer want to use a particular environment variable, select it in the Environment Variables window. Then, press Delete. Windows does not ask for any confirmation of this action. Therefore, if you have changed your mind, you must press Cancel, so that the removal is not applied. If you want the deletion to go ahead, press OK.
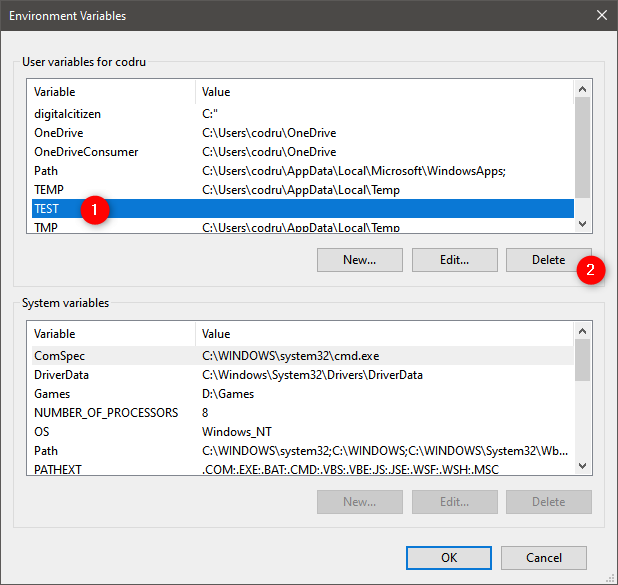
How to delete an environment variable in Windows 10
How to delete an environment variable from Command Prompt
To delete an environment variable from Command Prompt, type one of these two commands, depending on what type that variable is:
- REG delete “HKCU\Environment” /F /V “variable_name” if it’s a user environment variable, or
- REG delete “HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Session Manager\Environment” /F /V “variable_name” if it’s a system environment variable.
For example, we typed REG delete “HKCU\Environment” /F /V “TEST” and our TEST environment variable was gone from the user’s profile.
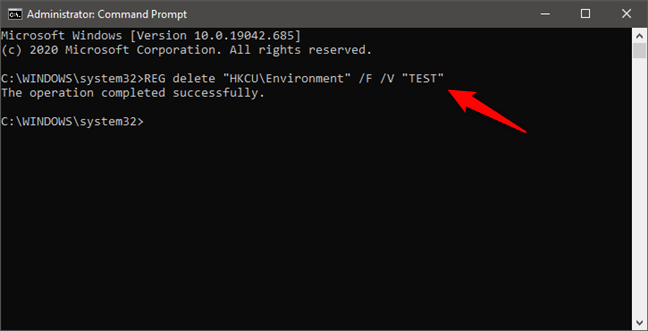
How to unset an environment variable in Windows using Command Prompt
How to delete an environment variable from PowerShell
To unset and delete an environment variable from PowerShell, type the command:
- [Environment]::SetEnvironmentVariable("variable_name", $null ,"User") if it’s a user profile variable, or
- [Environment]::SetEnvironmentVariable("variable_name", $null ,"Machine") if it’s a system-wide variable.
For example, we typed [Environment]::SetEnvironmentVariable("TEST", $null ,"User") and this environment variable was gone from the user’s profile.
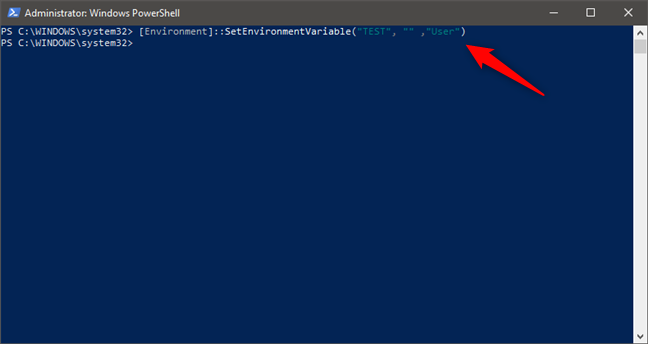
How to delete an environment variable from PowerShell
That’s it!
Why did you want to learn how to edit and delete environment variables in Windows?
You now know how to do all that. But why did you want to change or edit environment variables? Was it because there were leftover variables on your system from certain apps that you no longer used? Or was it because you have a special setup, and you need to work with environment variables? Let us know in the comments section below.