Security is essential in any digital environment, so to make it easier for users to manage permissions and other user accounts, Windows offers a useful feature called user groups. Although it may seem a bit intimidating at first, this feature is not that hard to understand and use, and it might just save you a lot of time and energy when managing multiple accounts. Let's get into some more detail and see what user groups are and how you can use them to your advantage on any computer with Windows:
Contents
- What is a user group in Windows?
- Why does Windows have user groups?
- What types of user groups are found in Windows?
- Who can manage user groups?
- How to see the Windows user groups that exist on your computer
- How to see which Windows user groups your user account belongs to
- Do you have any other questions about Windows user groups?
What is a user group in Windows?
To understand what a user group from Windows is, you must first know what a user account is. The (very) short definition is this: a user account is a collection of settings used by Windows to understand your preferences. It’s also used to control the files and folders you access, the tasks you are allowed to perform, the devices and resources you are allowed to use, and so on. User accounts are also the only way of authenticating and receiving the authorization to use your Windows device. This brief definition should be a good start for understanding what user groups are in Windows. However, if you want more information about user accounts, what they are, and what are they useful for, first read about what a user account or a username is in Windows.
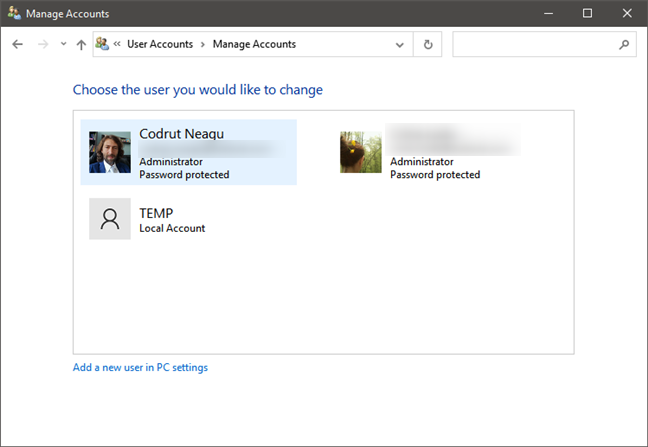
List of user accounts in Windows 10
To expand on this knowledge, in Windows operating systems, a user group is a collection of multiple user accounts that share the same access rights to the computer and/or network resources and have common security rights. This is why you will often hear IT professionals refer to user groups as security groups. User groups can be categorized into three different types:
- Local groups - are the user groups that exist on your Windows computer or device. They are defined locally and can be managed from the Local Users And Groups (lusrmgr.msc) tool. These are the user groups that home users work with and the ones that we’re going to talk about in this article.
- Security groups - have security descriptors associated with them. Security groups are used in Windows domains with Active Directory.
- Distribution groups - are useful for distributing emails for users that belong to domains with Active Directory.
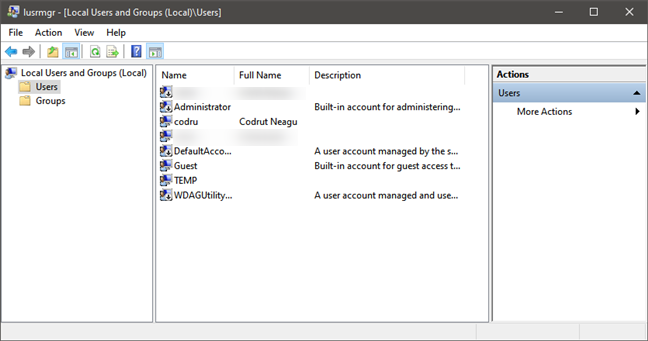
List of user accounts shown by lusrmgr.msc
The Security groups and the Distribution groups are user groups that are used in business environments and company networks. For instance, you can encounter security user groups at your workplace, especially if you're working in a big company that has multiple departments with lots of computers, both mobile and workstations. System administrators utilize groups to limit user access to features of the operating system, which they shouldn't modify or set different levels of access for the applications that are available on the company's network.
Although the correct term for the user groups that we’ll be covering in this article is local user groups, we’ll use the simpler form of user groups to make the information shared below easier to understand.
Why does Windows have user groups?
Let’s say that, for example, you want to give your relatives the option to use your computer when they drop by for the holidays. You may want to create an account for your 7-year-old cousin, so he can play some games, one for your aunt, and one for your uncle. However, you don't want to give them administrative rights, so that they don't change essential settings in your operating system or gain access to your sensitive personal information.
To handle the situation in an elegant fashion, you can group all their accounts in a user group and grant them the same security privileges without having to set each account's rights individually.
User groups are an essential security feature that is aimed primarily at simplifying the management of large numbers of users. Read how to create a new user on Windows 10 and how to add a user to a group for further information.
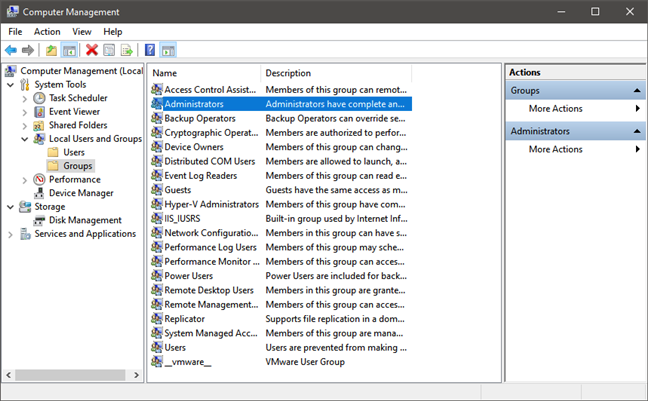
Windows 10 Local Users and Groups
The strength of user groups resides in the fact that they offer a centralized way of managing multiple user permissions without the need to configure each account separately. When a user group receives access to a particular resource, all the user accounts that are part of that group receive access to the resource in question. Note that although you can and must use a user account to log in to a Windows computer or device, you cannot use a user group to log in.
What types of user groups are found in Windows?
There are many types of user groups that exist, by default, on all Windows computers. Here are the most important and useful default user groups in Windows:
- Administrators: the users from this group have full control of the Windows computer and everything on it, including other user accounts.
- Backup Operators: user accounts from this group can back up and restore files on the Windows computer, regardless of those files’ permissions.
- Guests: users from this group have temporary profiles set when they log on, which are automatically deleted when they log out.
- Power Users: can do almost everything administrators can, including creating other user accounts or even deleting them. However, they cannot change the settings for the Administrators group. This is also the answer to a question we were asked by some people: which type of user group provides backward compatibility with Windows XP?
- Users: are the standard user accounts. They are the users who can do all the typical things people do on their computers, like browsing the internet, using the apps installed, accessing the files on the computer, or printing. However, standard users cannot do things like creating other user accounts, they cannot install applications on the computer, and they cannot install a printer on the computer.
Third-party software and services can also create user groups used for various services. The most common example is virtualization software. For example, some VMWare products such as VMware Converter create user groups like __vmware__ and ___vmware_conv_sa___, as well as ___VMware_Conv_SA___ accounts, which are used to run virtual machines and standalone server jobs.
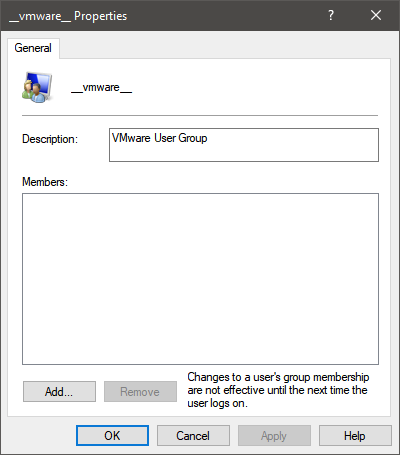
__vmware__ user group in Windows 10
There are other types of user groups found by default in Windows operating systems. If you want to know more about all of them, read How to manage local users and groups in Windows 10 using lusrmgr.msc.
Who can manage user groups?
By default, the only users who are allowed to make changes to user groups are the ones who belong to the Administrators or the Power Users groups. In the image below, you can see that the only members of the Administrators group are the users Administrator and Digital Citizen.
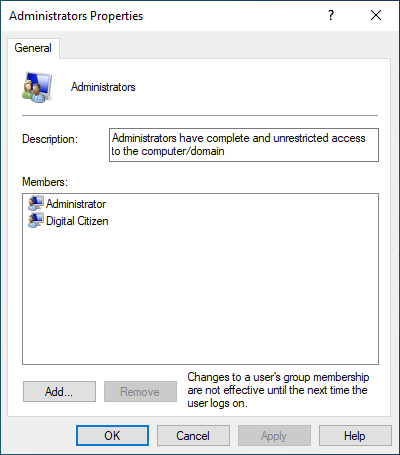
Administrators group in Windows 10
If you try to make changes to a user group while logged in with a user account that's not part of the Administrators or Power Users group, you will get the following error: “Access is denied.”
Standard users aren't allowed to make user group changes
How to see the Windows user groups that exist on your computer
You can manage existing users and user groups only from an administrator account. In other words, if you want to view and modify user groups, you must log in with a user account that is part of the Administrators user group.
Once logged in with the right account, open the Computer Management tool, and use the Local Users and Groups snap-in to see the list of Groups. However, take notice of the fact that this snap-in is available only in some Windows editions: Windows 7 Professional, Ultimate and Enterprise, Windows 8.1 Pro and Enterprise, and Windows 10 Pro and Enterprise.
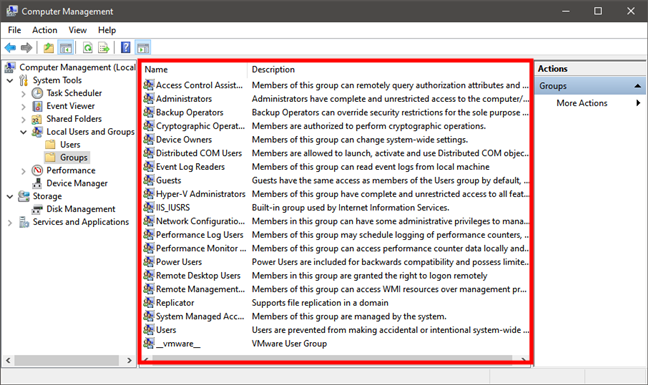
List of user groups in Windows 10
You can also get a list of all the local groups on your computer by running the net localgroup command in PowerShell or Command Prompt.
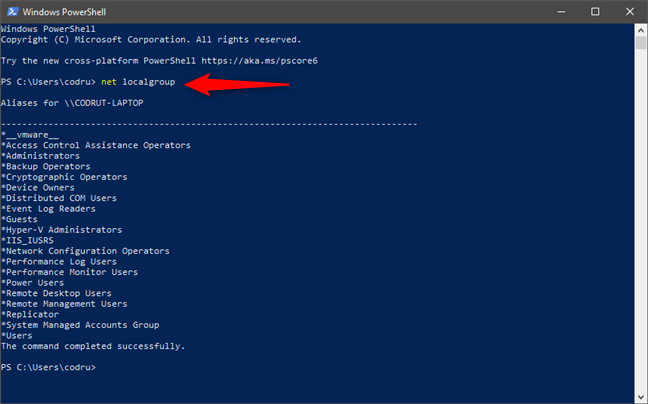
The net localgroup command shows all the defined local user groups
How to see which Windows user groups your user account belongs to
The easiest way to learn which user groups your user account belongs to is through the use of the whoami /groups command. Open Command Prompt or PowerShell, type whoami /groups, and press Enter.
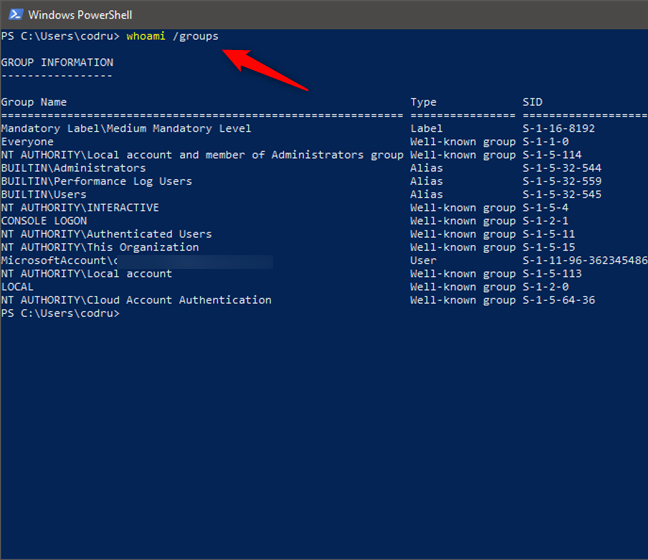
The whoami /groups command shows the list of groups a user belongs to
This tool shows the list of the groups your user account is registered to. To determine what user groups a user account is part of, you must run whoami /groups while logged in with that specific user account.
Do you have any other questions about Windows user groups?
User groups are a powerful feature that can be very useful when you have computers used by two or more people. It saves you a lot of time and effort when managing multiple user accounts and provides a centralized way of doing it. Have you worked with user groups in Windows? How useful did you find them? We would like to hear more in the comments section below.