With increasingly demanding games and streaming needs, many people struggle with the constraints of slow hardware. Hyperthreading is there to help in these situations. It increases the speed of your CPU, but there are some downsides to consider as well.

There has been some speculation that hyperthreading on Intel CPU can make your system vulnerable to hacks. Intel claims that this is not the case. But regardless of security issues, it’s best to disable this feature if you want to avoid straining from your CPU.
Some Notes Before You Start
Hyperthreading is an Intel specific term that describes simultaneous multi-threading. With that definition out of the way, it can be done on Intel and AMD CPUs. That said, certain processors are not compatible with hyperthreading, which means there’s no way to do it in the first place.
There are some models that are hyperthreaded by default and you need to disable the feature from the BIOS. This isn’t too difficult to do, but you do need to be at least familiar with the system. The exact steps for disabling this feature may vary depending on the system you are using and the CPU in question.
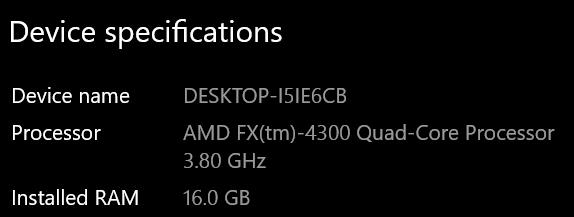
Depending on how new you are to working with processors, your exact model can be found using the Win+I keyboard command, clicking on System, then About.
The following section provides some basic steps that apply in most cases. But should you run into a problem, you can always consult the help page of the CPU’s manufacturer.
Disabling Hyperthreading
As mentioned, first you need to enter the BIOS. Although Windows 10 allows you to do so from the system, it’s easiest to power off the computer, turn it on, and press a certain set of keys. This depends on the machine you are using. For example, Dell computers use F2 or F12, but it’s F10 on HP. On some models, you just need to press the Delete key on boot up.

Once inside the BIOS, you need to navigate to the right host for the given system. Right off the bat, this might sound as intimidating, but there’s a menu or configuration tab you should find with relative ease. The label you are looking for is Processor and it might be located in one of the sub-menus. Take your time until you find Processor and then hit Enter to access the settings.
When you get to the Processor menu, select Properties. In most cases, a dialogue box will appear, allowing you to choose to turn hyperthreading off (or on). After you disable the feature, go to the Exit menu and select Exit Saving Changes. The name or layout may differ on your computer.
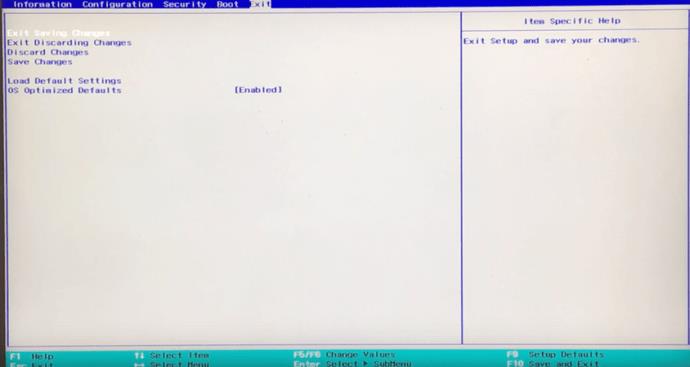
Note: This applies to Intel processors, while AMD ones use slightly different labels. For example, you navigate to a Logical Processor instead of just a Processor.
How Does Hyperthreading Speed Up Your System?
Simply put, hyperthreading creates more room for your data to travel. Once you enable the feature, you allow the data to move along two tracks instead of one. The data gets separated and then processed by the computing depot, which makes your computer run faster.
Without hyperthreading, your processor gets one program per core at a time. Hyperthreading means you can get multiple programs per CPU, which allows you to basically turn each core into two processors.
The system that provides this is called parallel computing or superscalar architecture. This means your computer is able to cope with several instructions from multiple threads (or tracks).

How Many Cores Are There?
Having more cores on your CPU means faster processing. The more cores there are, the less likely you are to need hyperthreading. But make sure you know the real facts about the hardware you have.
For example, Intel hints at the number of cores by labeling its processors i3, i5, i7, etc. But in reality, you only get four cores on some i7 processors, and i7 Core processors from the Extreme series may come with up to eight cores.
If you want to do heavy-duty image or video processing, or 3D rendering, you might benefit from hyperthreading your processor, even if it’s i7.
Does Hyperthreading Always Work?
For gaming and streaming purposes, hyperthreading usually does the trick. You get a significant improvement (up to 30%), especially if you are on a slower processor, such as i3 or i5.
However, the speed might not improve in other applications. In part, this is because certain programs cannot efficiently send multiple data strings into a threaded core.
Frequently Asked Questions
Should I disable hyperthreading?
There’s actually a lot of debate here on whether or not you should disable hyperthreading. Based on our tests, it really depends on too many factors (such as how many cores you have, what you’re doing, etc.) to give a straightforward answer.u003cbru003eu003cbru003eThese days, most PCs will automatically stop and begin hyperthreading as necessary to speed things up. Some users have complained of heating issues after disabling hyperthreading while others say their system actually runs cooler.u003cbru003eu003cbru003eAside from the fact that you could be putting your computer at risk according to several experts, you should only consider disabling hyperthreading when it’s absolutely necessary to do so. u003cbru003eu003cbru003eThis is really one of the things you’ll need to test out to get the best answer based on your system and the software you’re running.
What if I don’t see the option to turn it off?
This is more common on laptops but often times the option just simply doesn’t exist. Particularly on Asus laptops, there is no option to disable hyperthreading but you may find some workarounds online in tech forums.u003cbru003eu003cbru003eDepending on which processor you have, the location in BIOS may be different than what we’ve mentioned above. If you don’t see the option to turn off hyperthreading it’s best to research your exact model for more help.
The Final Thread
This article should provide you with enough information to avoid trial-and-error when disabling hyperthreading. You can easily turn the feature on using the same steps. The important thing to note is not to rush things with the BIOS, especially if you are using it for the first time.