The evolution of technology brings breakthroughs in the visual experience but also from the graphics to life, nvidia's new Ray Tracing technology is the answer to that development when the company launches the line of graphics cards . New generation graphics based on their Turing architecture. So what is Ray Tracing ? Why say this is the technology of the future? Let's find out with WebTech360 in this article
What is Ray Tracing?
Ray Tracing is a technique of rendering (rendering) light by following light rays (trace means chasing, ray means light rays). You can imagine this technique like how you look up at the sun, tracking where its rays hit, what objects they hit and how it shines on the surrounding objects. Ray tracing recreates that process but in a digital environment.
In other words, ray tracing tracks the light absorbed, reflected, scattered and scattered by each object in the environment, and it applies not only to a beam of light from the sun but to any other light source. (for example: 2 light bulbs in the game room, the flickering fire of the fireplace in the game, the artificial light source is fixed when rendering 3D...).
Currently, Turing architecture with Ray Tracing is still a big question mark, expected to be a revolutionary turning point of the GPU market, such products are likely to be seen in most PCs in the future. or not, or is the price so high that few people can own and use it?
It is difficult to answer, because although there have been articles and reviews for the two GeForce RTX 2080 FE and GeForce RTX 2080 Ti FE series, we still have to wait, even for games that support high technology. of the card, here is ray tracing. In addition, Quadro professional graphics cards are also equipped with this new technology: Quadro RXT 8000, Quadro RXT 6000, Quadro RXT 5000, Quadro RXT 4000.

How Ray Tracing Works
The goal of ray tracing is to create more realistic lighting and more natural shading, and NVIDIA 's RTX series has achieved impressive results, at least in the launch demos. A wooden room with an open window will light up almost the whole room when using traditional lighting, and when ray tracing is on, places with direct light will be brighter than in the dark corners of the room. room. NVIDIA also showed how the flames in Battlefield V can haunt a character in the game and scorch car doors very realistically.
Light not only affects illumination, it also affects color, depth, and shadows. So when the lighting is simulated close to real life, the rest of the elements are also well done. The shaders in the current game look quite harsh and clear, lacking the slight transition between the light and dark patches, and ray tracing is the piece that makes this possible.
Ray Tracing Algorithm
Creating a simulation of the real world is a very complex undertaking. It includes many factors, like an infinite number of light beams, reflecting surfaces, passing through objects, all based on the molecular properties of each object, not to mention gravity and physical interactions. Simulating such an "infinite" thing using only the finite resources of the current computer is completely disproportionate and impossible.
We call a solution to the above problem "rasterization", instead of dealing with an infinite number of photons, the processing begins with polygons. More polygons mean faster processing speed, and rasterization is here to turn those millions of polygons into a specific image.
In short, it creates 2D prototypes and renders them on a pre-built 3D world. In it, 2D images made of polygons can cover the entire screen when viewed up close, but may cover only a few pixels when viewed from a distance, thereby creating pixels, textures and principles. light. Of course, one technique cannot cover the entire job.
Various techniques such as Z-buffer (a secondary buffer that tracks the depth of each pixel) speed up the process, creating a tool that makes the millions of generated polygons visible, sortable and handled as efficiently as possible. This can require millions or even billions of calculations per frame that only modern GPUs with processing speeds of teraflops can handle.
Ray tracing , approaches the above problem differently from R asterization , historically it has been around for about 50 years now. Turner Whitted currently works for NVIDIA , in the past sketching how to compute recursively tracking, resulting in impressive visuals including shadows, reflections and more. Of course, it's going to be a lot more complicated than rasterization.
Ray tracing involves detecting the direction of a ray (usually a ray of light) when projecting it into the 3D world. Suppose you want to build an object, the first thing is to determine the light rays that follow the polygon that makes up the object, then take into account the possible light sources, the properties of the polygon such as the material, flat or curved surface, in short, add or subtract light rays.
This process is then repeated for any other light sources, including light reflected from objects in the scene. It is so complex that many formulas are needed to make ray tracing possible, even for transparent, semi-transparent surfaces, e.g. glass or water . Everything must have a limit of artificial reflection, because even a ray cannot detect all the infinite number of photons.

The most commonly used ray tracing algorithm, according to NVIDIA , is BVH Traversal: Bounding Volume Hierarchy Traversal which speeds up the process by zoning objects for processing, in other words "divide and conquer" .
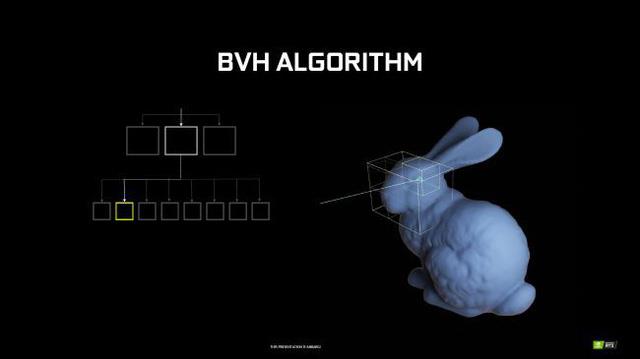
You can refer to NVIDIA's rabbit model which uses the BVH algorithm, which localizes each level, divides the parts into blocks, smaller and smaller until the algorithm results in a short list polygons, and then the job of ray tracing.
However, the amount of work to do when doing this work with software on the CPU or GPU is too high. An alternative is RT core, each RT core has built-in BVH structure algorithm, making it capable of processing work 10 times faster than CUDA core.
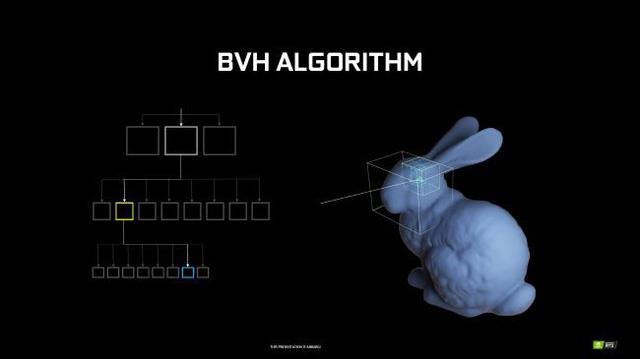
In addition, it must also be mentioned how many light rays are detected on a pixel, just one ray leads to tens or hundreds of calculations, but the more rays tracked, the work will be lighter, and the productivity will be high. than. Companies like Pixar, also use ray tracing technology to create animations.
A 90-minute movie with a frame rate of 60 FPS requires 324,000 images, each of which takes several hours computing the rays that are tracking each pixel. How is NVIDIA going to achieve such a real-time equivalent? I mentioned the appearance of RT cores above, but if that's not enough, the answer is that Tensor cores are only available in Turing architecture. For a simple example, taking a workload of FP16, Tensor cores reach 114 TFLOPS while FP32 and CUDA have only 14.2 TFLOPS.
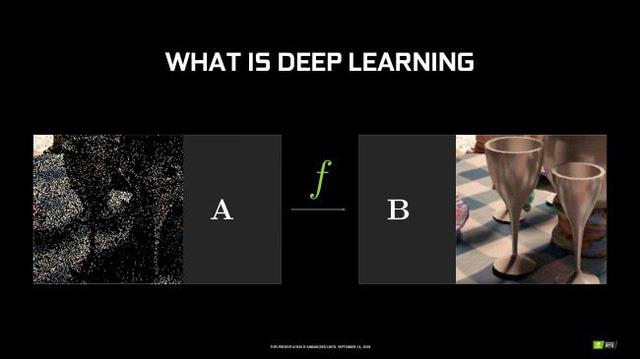
But why is Tensor core enough for ray tracing? It's AI and self-learning, in other words it's Deep Learning Super Sampling feature that allows the game to render at a lower resolution without AA, then the Tensor core will inherit and impact the frame , anti-aliasing for higher resolution.
In conclusion, big names in the rendering industry have stepped into ray tracing such as Epic, UE, Unity 3D, EA Frostbite. Microsoft even created DirectX Ray specifically for ray tracing. With RTX, this is really a big jump in the computer graphics industry, of course it is still not complete and within the next ten years to be able to put the RTX 2080 Ti in the market as a mainstream is completely. maybe.
Ray Tracing Technology on NVIDIA's Latest Graphics Cards
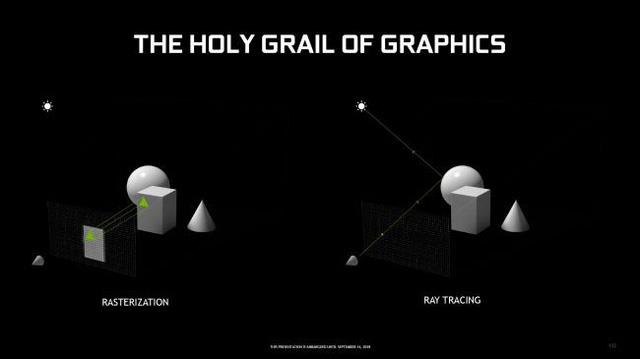
Current graphics technology from NVIDIA and virtually the entire industry is about simulating light and the behavior of light in a given scene, in a simpler way, called Rasterization. Like a painter paints, objects are rendered layer by layer, back to front, so objects in the foreground will obscure objects in the background.

Display difference between conventional Raster (left) and ray tracing (right).
However, this approach will be difficult when rendering the reflection, because the raster technique will not be able to track and render the light. It is often used in real-time scenes because current hardware is not enough to simulate the motion of complex scenes, for example in video games or 3D animations.
Meanwhile, ray tracing reconstructs the behavior of light as it hits surfaces, materials and moving objects.
Light as it passes through a scene can be rendered and rendered more complex. With ray tracing, you can simulate how light rays interact with objects, creating realistic reflections, refractions, and scattering effects in real time. Ray tracing can even detect and display refractors, reflectors, visualize the source of light in the scene and even the color of the light after it has passed through the subject.

In fact, this technique has been used in practice, with movies like Pixar's Monsters University, Marvel's Iron Man. But that was when it was used by professional users, but now it has been brought to general users – something that was impossible before.
This deserves to be called a feat of NVIDIA because ray tracing requires a huge amount of computing power. NVIDIA CEO Jensen Huang said it was "the biggest leap we've ever made in a generation (GPU cards)."
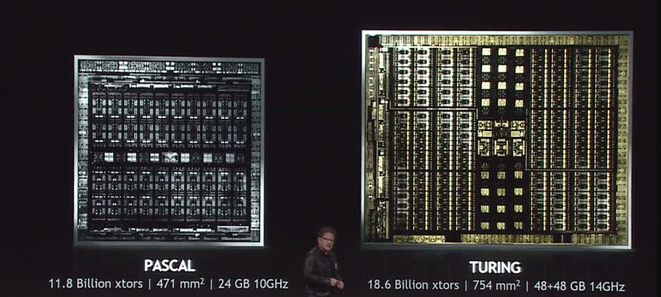
NVIDIA's way of solving the problem is to use the new Turing architecture in the newly released GPUs. This architecture is designed to solve the processing problem. The dedicated ray tracing cores are also equipped with Tensor Cores, which are able to use AI to infer the "real-time" portion of the image – the most computationally intensive problem of this technique. So the GPUs are able to emulate 6x faster than the previous Pascal platform (on GTX 1080Ti).
This is truly a huge leap in graphics technology and it's exciting to think that studios and individuals will now be able to extend the use of this ray tracing technique to applications in animation, Science games and simulations.
Hopefully, Ray Tracing technology will be more and more developed, then we will experience even more beautiful image quality, but at the present time it is really difficult for you to experience Ray Tracing for other users. terrible games because they require huge software. If you need advice on Ray Tracing gaming configuration, please contact WebTech360 .
Synthesized from: Genk.vn