How to Copy Partition to Another Drive in Windows 11/10/8/7
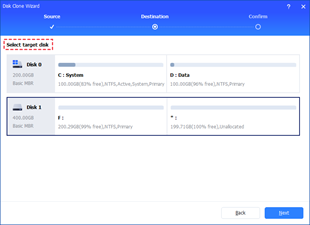
In Windows 11, 10, 8, and 7, you can quickly copy a partition to a different drive using the flexible disk cloning tool AOMEI Partition Assistant.
Windows 11 can handle many different power states. Here's how to check the supported power status on a usable Windows 11 computer.
Most PC users know the common power states such as On, Off, Sleep and Hibernate. However, computers can handle power in many ways. Understanding these power states can help you understand how your PC works and provide you with some more useful ways to use your computer.
However, not all power states are available on the computer. You need to check the available power status based on the hardware.
How to check available power status in Windows 11
You can find the available power statuses on your computer using Command Prompt.
powercfg /availablesleepstatesYou will see two lists of power statuses. One is the list of supported power states, the other is the unsupported power states.
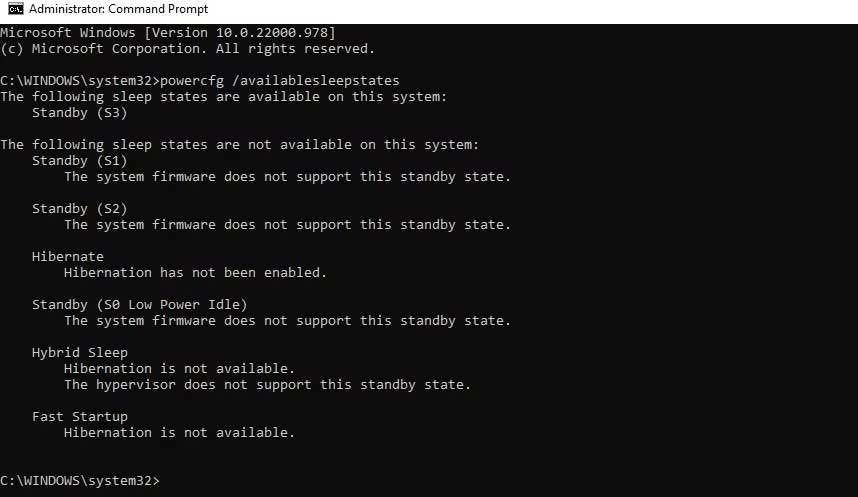
All Windows 11 power states
S0: Working State
S0 represents working status. This is the state of the computer when you can use it.
S0 Low-Power Idle: Sleep (Modern Standby)
Modern Standby is an upgrade to the S3 source model. It allows you to turn on devices faster than S3, providing a seamless experience when using a modern device. This mode is typically supported on System on Chip (SoC). However, there are still exceptions. If your computer supports S0 low power idle mode, it will not support S1, S2, or S3 mode.
S1, S2, S3: Sleep Power States
The “Sleep” state is where one or more components on the computer are turned off or go into low power mode.
Sleep power state S1 stops the CPU, the rest of these components are turned off or continue to run in low power mode, and RAM maintains power.
The sleep power state S2 stops providing power to the CPU, other components are turned off or continue to run in low power mode, and RAM maintains power.
S3 is a standby state where the CPU has no power, but RAM maintains power and refreshes it at a low rate. Other hardware components such as hard drives and fans will temporarily stop operating.
Your device may also support “Hybrid sleep” mode. Here, you can save this session. If the computer loses power while in sleep mode, you can continue what you just left off.
S4: Hibernate
This mode is different from Sleep because hibernation saves the contents of RAM and operating system state to the hard drive and turns off the power of all connected devices. When you turn your computer back on, you can directly start work from where you left off before going into hibernation.
S5: Soft Off Power State
S5 is the “soft off” state. Only components like the power button have a trickle of current. No other components draw power in this state, and the computer is not performing any computational tasks.
G3: Mechanical Off
Shutdown state is also the state where the computer is completely turned off like in S5. However, the power supply is completely removed via a mechanical switch. No power to any hardware components, including the power button. This state is usually only necessary when you want to disassemble the computer. Note that the real-time clock can still continue to run using a small battery.
Above are the things you need to know about the power status on your computer . Hope the article is useful to you.
In Windows 11, 10, 8, and 7, you can quickly copy a partition to a different drive using the flexible disk cloning tool AOMEI Partition Assistant.
Driver Booster 12 Free is an effective tool that will keep your computers drivers up to date, which will make the system run faster and more reliably. This driver updater from IObit keeps your PC running at its best by checking for lost, out-of-date, or broken drivers immediately.
In an era where digital efficiency is paramount, Advanced SystemCare 17 Free emerges as a beacon for those seeking to enhance their PC's performance.
Summary of Movies & TV application shortcuts on Windows 10, Summary of Movies & TV application shortcuts on Windows 10 to bring you a great experience. Maybe
How to fix Messages Failed to Load error on Discord for Windows, Discord isn't fun if you can't read what other people write. Here's how to fix Messages error
How to display the This PC icon on the Windows 11 desktop, During the process of using Windows 11, many users need to access This PC (management).
How to find information in the Windows Registry quickly, Do you find it difficult to find information in the Windows Registry? So below are quick ways to find the registry
How to limit the number of failed login attempts on Windows 10. Limiting the number of failed password login attempts on Windows 10 helps increase computer security. Here's how
How to create fake error messages in Windows, Windows can come up with some pretty creative error messages but why don't you try creating your own content for them to make fun of?
Ways to open Windows Tools in Windows 11, Windows Administrative Tools or Windows Tools are still useful on Windows 11. Here's how to find Windows Tools in Windows 11.
How to fix Windows Quick Assist not working error, Windows Quick Assist helps you connect to a remote PC easily. However, sometimes it also generates errors. But,
How to pin Word, Excel and PowerPoint files to the corresponding app icon on the Windows 11 taskbar, How to pin Office files to the taskbar icon on Windows 11? Invite
How to fix the error of not being able to install software on Windows, Why can't you install apps or software on Windows 10/11? Here's everything you need to know about how to fix it
Instructions for deleting or changing the PIN code on Windows 11, In Windows 11, the PIN code is a very useful and convenient security tool for users. However some people
How to fix There Are Currently No Power Options Available error in Windows 10, Can't select power mode in Windows 10, what should I do? Here's how to fix the error
The simplest way to fix Photos app errors on Windows 10, what should I do if Microsoft Photos doesn't work? Don't worry about ways to fix Photos app errors on Windows
Instructions for installing shortcuts to switch input languages on Windows 11. During the process of using Windows, users will often have to switch between methods.
How to check power status is supported on Windows 11, Windows 11 can handle many different power states. Here's how to check the power status
How to switch from 2.4GHz to 5GHz in Windows 10, If you want to find a quick and simple way to speed up the Internet, changing the WiFi band from 2.4GHz to 5GHz may help.
How to fix Not Enough Memory to Run Microsoft Excel error on Windows, Are you having an error of not enough memory to run Microsoft Excel? So, how to fix Not Enough Memory error