Why Reliability and Flexibility Are the Cornerstones of Great Tech

In the fast-moving digital landscape of the modern world, businesses can no longer afford to rely on systems that are only strong in one area.
Photoshop can create a series of basic 3D shapes using 2D layers as a starting point. After creating a 3D object, you can move it into the 3D space, change the rendering configuration, add lighting or merge it with other 3D layers.
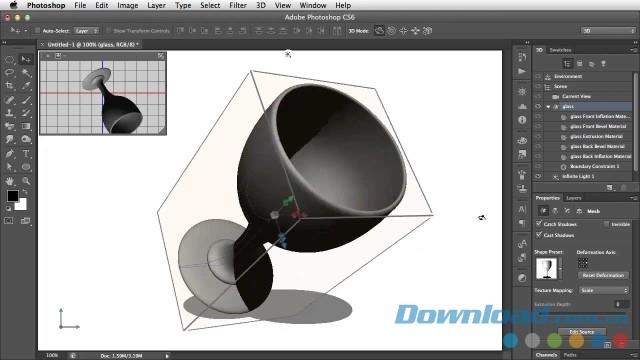
Note : You can add a 3D postcard to an existing 3D scene to create a surface that displays shadows and reflections from other objects in the scene.
1. Open the 2D image and select the layer to convert to a postcard.
2. Select 3D> New 3D Postcard From Layer .
3. To add a 3D postcard as the plane of the 3D scene, merge the new 3D layer with the existing 3D layer containing other 3D objects, then align it as needed.
4. To retain new 3D content, export the 3D layer as a 3D file format or save it as a PSD file.
Depending on the type of object you choose, the 3D model may contain one or more meshes. The Spherical Panorama option maps the panoramic image into a 3D sphere.
1. Open the 2D image and select the layer you want to convert to 3D.
2. Choose 3D> New Shape From Layer , and choose a shape from the menu. Shapes include single mesh objects such as donuts, spheres, hats and many other mesh objects such as cones, cubes, cylinders, soda cans, or wine bottles.
Note : You can add your own custom shapes to the Shape menu. Shapes are Collada (.dae) 3D model files. To add a shape, place the file in the Presets \ Meshes inside the Photoshop folder.
3. Use the Spherical Panorama option if using panoramic photos as a 2D input. This option converts a 360-degree image into a 3D layer. After converting to a 3D object, you can paint on difficult-to-reach panoramic areas such as poles or lines.
4. Export 3D layer as 3D file format or save in PSD format to retain new 3D content.
New Mesh from the Grayscale command converts a grayscale image into a depth map that translates brightness values into surfaces of different depths. Lower values create areas that rise above the surface, higher values create lower areas. Photoshop then applies the Depth Map to one of the four possible geometries to create a 3D model.
1. Open a 2D image and select one or more layers to convert into a 3D mesh.
2. (Optional) Convert the image to Grayscale mode ( Image> Mode> Grayscale or Image> Adjustments> Black & White to adjust the grayscale conversion mode).
Note : If importing RGB images when creating Mesh, blue channel is used to create depth map.
3. (Optional) Edit Grayscale images as needed to limit the light value.
4. Select 3D> New Mesh From Grayscale , then select a desired Mesh.
Photoshop creates a 3D layer containing the new Mesh. It also creates Diffuse, Opacity and Planar Depth Map texture maps for 3D objects, using Grayscale or the original color layer.
You can reopen the Planar Depth Map as a Smart Object at any time and edit it. When saved, the Mesh will be regenerated.
Note :
The Opacity texture map does not appear in the Layers panel, because that map uses the same texture file as the Diffuse map (the original 2D layer). When two structure maps refer to the same file, the file will only appear once in the Layer panel.
Using the Photoshop Animation timeline , you can create 3D animations in space and change its appearance over time. You can apply effects to any of the following properties of a 3D layer:
For high quality animation, you can build each animation frame by using Render for the Final Output render settings .
Hope this article is helpful to you!
In the fast-moving digital landscape of the modern world, businesses can no longer afford to rely on systems that are only strong in one area.
Looking to create engaging product demos in minutes? Look no further! This guide will introduce you to the best tool for the job.
Discover the latest updates in Zooper Widget for Android. Zooper Widget is a compact, highly customizable, and battery-friendly widget with endless possibilities.
Lipp for iOS, alongside Dubsmash and Musical.ly, provides iPhone and iPad users with a new platform to create lip sync videos and dub videos readily.
Learn how to share audio using TeamViewer, including the latest updates for 2024 and 2025, making remote communication more effective.
Learn the latest tips on how to pet a cat in Adorable Home for optimal gameplay in 2024 and 2025. Discover what positions give you hearts.
Explore the latest features of OrangeHRM Open Source, a free HR management system tailored to meet evolving business needs in 2024 and 2025.
Fix IDM not catching file download links. Discover solutions for downloading videos, music, and more with the latest IDM updates in 2024 and 2025.
Discover the latest version of The File Converter for Android, an application that converts various file formats efficiently.
Explore the latest features of Zalo Web, allowing users to chat and connect seamlessly on various browsers without installation.
PDF Password Remover is a powerful tool for removing passwords and restrictions from PDF files. Download the latest version for 2024 to experience enhanced features.
Step-by-step instructions to completely remove Internet Download Manager (IDM) from your system in 2024 and 2025. Learn to uninstall IDM effectively and cleanly.
Discover Mindjet MindManager, an innovative software that helps individuals and teams streamline their work processes through effective mind mapping and project management.
Su DoKu 2.0.0 is an advanced Sudoku game design software that captivates enthusiasts with its simplicity and functionality. Download now and challenge yourself with Sudoku puzzles.
Discover the new features of Google Photos for Android in 2024 and 2025, including faster backup and advanced search capabilities.