What is 3uTools? How to install and use 3uTools in detail

3uTools supports users to manage utility applications more than the traditional way. Easy-to-use interface, will bring interesting experiences to you.
If you are looking to buy yourself a PC, first you should learn a little about a few specific slang words here, Chipset , in Vietnam, users are a bit confused between the words CPU and Chipset. that's the processor, from which we often hear called chipset, buy Pen4, pen3, .... ie buy CPU. In fact, this is a misnomer and chipset is a very special thing that is available on both motherboards and discrete graphics cards. So what is a Chipset ? Let's learn more about WebTech360 as well as the history of this word.
When it comes to personal computers (PCs) based on the Intel Pentium system, the word " chipset " usually refers to two main board chips: the northbridge and the southbridge. The chip manufacturer is usually independent of the board manufacturer. Examples of chipset manufacturers for PC boards include NVIDIA, ATI, VIA Technologies, SiS, Intel and AMD.
In the early days of computer development, motherboards were often packed with integrated circuits (ICs) with separate functions. IC is one or more chips that control each component of the system such as mouse, keyboard, video card, sound...
If on a motherboard with a small size, but with dozens of ICs, it is clear that the production and operation of the motherboard will not be efficient. Therefore, computer engineers found a better system, they began to integrate single chips together, greatly reducing the number of control chips on the motherboard.
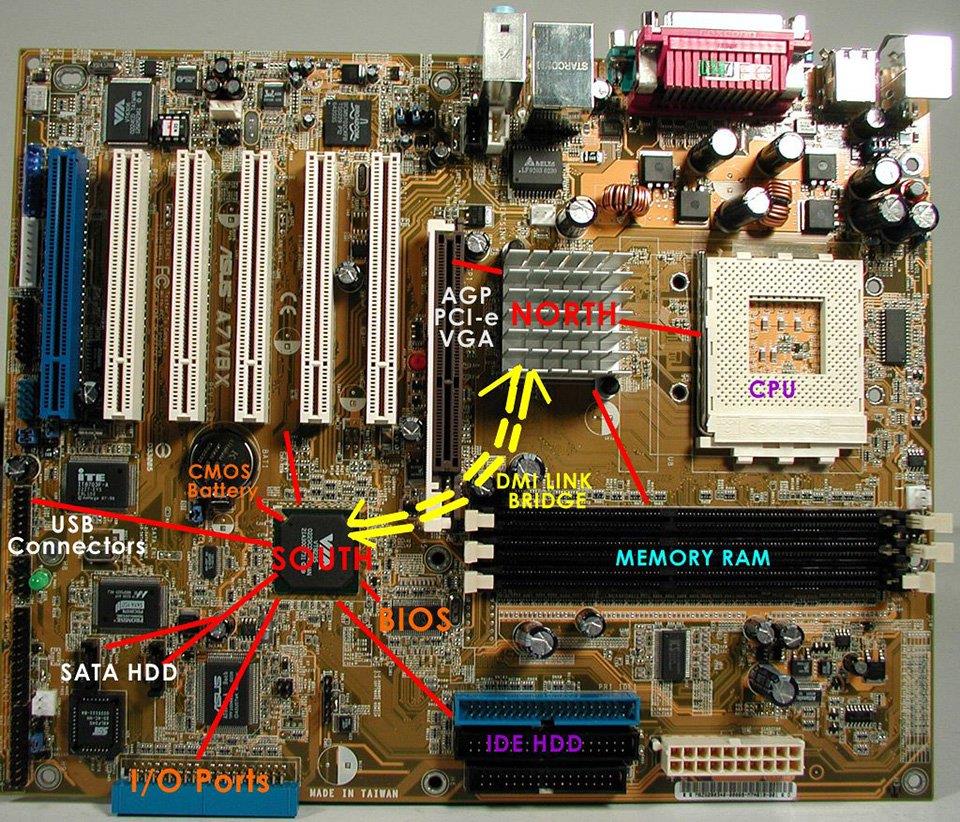
Standard for data transmission between peripheral devices on PCI (Peripheral Component Interconnect) motherboards , a new concept was born that is bridge.
Instead of a series of chips with their own function, the boards are equipped with a northbridge and southbridge chip. The two chips at the ends of the board hold very different tasks.
Northbridge (northbridge) got this name because it is located near the top, north end of the motherboard. It is responsible for connecting directly to the CPU and acts as an intermediary with the higher-speed hardware in the system. Includes RAM, PCI Express microcontroller and on older motherboards also AGP (Accelerated Graphics Port) microcontroller.
If these pieces of hardware want to talk to the CPU, they are forced to "pass" through the northbridge.
Southbridge, on the other hand, is located at the other or south end of the motherboard and it is responsible for controlling the operation of slower hardware such as: PCI expansion, Sata and IDE connections, USB ports, ports. audio, network ports... And in order for these hardware to communicate with the CPU, they must first go through the south bridge, but then to the north bridge and then the CPU.
The traditional northbridge and southbridge chipset designs have obviously also improved over time and from the step of forming the chipset concept as it is today.
The north and south bridge architecture gave way to a simpler system with only one chip. Some components: Memory, graphics card microcontroller... are now integrated and handled directly by the CPU.
Therefore, the priority control functions go to the CPU and the rest of the tasks are left to a chip like the southbridge.
All control components such as memory storage microcontrollers (SATA ports), networking, audio, etc. are managed by a single component. Instead of going from the south bridge to the north bridge and then to the CPU, all the rest of the hardware in the system only needs to communicate via PCH or FCH and then to the CPU . The result is significantly reduced latency and a more responsive system.
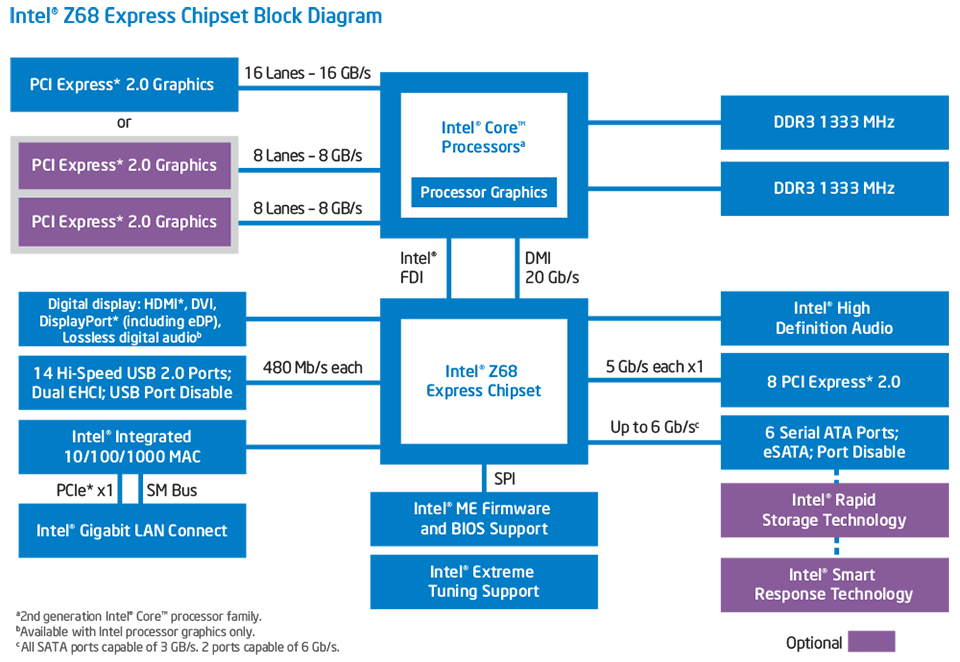
The chipset determines three things: hardware compatibility (such as the CPU or RAM you can mount on the motherboard), expansion options (how many devices you can attach via PCI port), and overclocking capability (OC). A little more detail:
First CPU, second chipset - these 2 components are always studied and chosen by us first, but the chipset always goes with the motherboard, so it can be said to choose the CPU first and then the motherboard later.
Once we have the chipset or motherboard, we will know how to choose the rest of the hardware, such as what type of RAM (DDR3 or DDR4), high or low speed; what hard drive and how many can be mounted; graphics card options and whether or not to support multiple cards (SLI or CrossFire setup) and other expansion card options.
Because of this diversity, the chipset also has many versions, the most advanced version of course supports more things and of course more money.
The chipset determines the expansion hardware options by means of the bus. Hardware components and peripherals connect to the motherboard via buses.
All motherboards support different types of buses, and each bus type has different speeds and bandwidths. We can divide the bus into two types: the internal bus and the external bus.
PCI Express (PCIe) is a typical internal bus and it exploits lanes for components such as expansion cards (graphics cards, sound cards, network cards …), RAM to communicate with the CPU and vice versa. In the simplest way, a lane is two pairs of wires, one sending data and the other receiving data. Thus, PCIe x1 will have 4 wires, PCIe x2 will have 8 wires… The more wires, the more data is exchanged. The PCIe x1 connection achieves a data transfer rate of 250 MB/s each way, PCIe x2 is 500 MB/s … Regarding the PCIe versions, there will be a separate post, these parameters correspond to the first generation PCIe i.e. the first generation PCIe. PCIe 1.x, the latest generation of PCIe is PCIe 4.0, one lane has a speed of nearly 2 GB/s.
The number of lanes available on the motherboard depends on the capabilities of the CPU and the motherboard itself. As an example, many Intel desktop CPUs support 16 lanes, and some of the newer, high-end CPUs support 28 to 40 lanes. Meanwhile, motherboards using the Z170 chipset usually provide 20 extra lanes. So with a CPU system that supports 16 lanes and a motherboard with 20 lanes, we have a total of 36 lanes.
Therefore, if you attach to this system a graphics card using PCIe x16, it will use up to 16 lanes. If you attach 2 cards that run the double bridge, both can run together at full speed but you only have 4 lanes left for other components. And if you intend to mount a variety of expansion cards then you need to consider the CPU and chipset support. If you run out of lanes and you still have an empty PCIe slot, when you add more cards, it won't work.

So now that you know about the chipset's determining role in hardware compatibility and scalability, now it's overclocking. Overclocking simply means pushing the clock of the hardware gods higher than the default clock. Proportional to speed are power consumption and heat production, which can cause system instability and shorten component life. As a result, the system will need better heat dissipation, such as water cooling and high-end power supplies.
The problem is that only certain types of CPUs can be overclocked, typically the K series from Intel and AMD. Furthermore, only certain chipsets support overclocking and some require special firmware to unlock overclocking capabilities. So if you want to overclock your computer, right from the moment you choose to buy hardware, you must find the right motherboard that uses an overclockable chipset.
Chipset that supports overclocking is required to be able to control the essentials during overclocking such as voltage, multiplier, clock ... in UEFI or BIOS to be able to push CPU speed higher than designed. If the chipset cannot overclock, these features will not be available or if they are, they will not be available and you will only be able to use that CPU at the speed set by the manufacturer.
Hope this article let you understand the importance of Chipset to other components such as CPU, GPU, ... and many other components. If you are in need of building computer configuration, please contact WebTech360 for good advice.
3uTools supports users to manage utility applications more than the traditional way. Easy-to-use interface, will bring interesting experiences to you.
Rendering is the process of creating an image from a model into a movie scene or image using computer software.
The CPU is the data processing center, or simply understood, it is the brain that controls most of the rest of the components in a computer.
The GPU is the processor that handles graphics-related tasks for the CPU's central processor. Features on GPUs go far beyond basic graphics drivers like Intel's GPU
Flyer is a form of advertising, a marketing product that has existed for a long time, also known as leaflets, product marketing brochures.
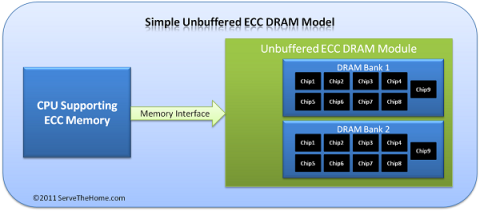
ECC RAM is a type of RAM that has the ability to control the flow of data accessed in it to help automatically correct errors. ECC RAM has very high stability which helps you to reduce risk.
Ray Tracing is a technique that helps a computer create an image by tracing the path of light through pixels on the same image plane.
Hyper threading is a hyper-threading technology and is known as Intel HT technology by globally famous technology manufacturer Intel.
The VRM circuit is the voltage regulator in the motherboard. With the presence of VRM, the CPU and GPU will be provided with clean power to operate stably.
On the quality screen, they integrate a technology called V-Sync, FreeSync. Let WebTech360 explain to you about V-Sync, what is FreeSync?
Anti-aliasing is the main adjustment mode to help objects and people become softer and not angular, the game experience will also be better.
Animation is an age-old method in which people make motions of images based on still images.
Footage is unedited raw footage and footage. You can understand that footage is all the components that make up a video, and footage is very diverse.
Storyboard is a storyboard, consisting of a series of illustrations and accompanied by notes about what is going on, carrying the content of the story.
Tired of the frustrating Microsoft Teams download failed due to unexpected error? Discover quick, step-by-step fixes to resolve it fast and download Teams smoothly on Windows, Mac, or web. No tech skills needed!
Struggling with Microsoft Teams network error: Check Your Connection? Discover proven step-by-step fixes to restore seamless video calls, chats, and meetings. Quick troubleshooting for instant results.
Tired of Microsoft Teams black screen in meetings? Get proven, step-by-step solutions to solve the video error instantly. From quick fixes to advanced tweaks—regain seamless video calls today!
Tired of Microsoft Teams crashing with DLL Error? Discover proven troubleshooting steps for missing DLL files like VCRUNTIME140.dll. Get Teams running smoothly in minutes—no tech skills needed!
Discover Microsoft Teams vs Zoom webinar features head-to-head: capacity, interactivity, security, pricing & more. Find the best platform for your next big webinar in this detailed comparison.
Struggling with Microsoft Teams chat not working on mobile? Discover quick, proven fixes for Android & iOS to get your chats flowing again. Step-by-step guide with troubleshooting tips.
Tired of the frustrating Microsoft Teams "Register" Account Error blocking your work? Discover proven, step-by-step fixes like clearing cache, resetting the app, and network tweaks. Get seamless collaboration back online today—no tech expertise needed!
Tired of Microsoft Teams crashing with "Hard Error"? Get the proven 2026 registry fix that resolves it in minutes. Step-by-step guide, screenshots, and tips for permanent relief. Works on latest versions!
Stuck with Microsoft Teams webhook integration errors? Discover proven troubleshooting steps, common error codes, and quick fixes to restore seamless notifications in Teams. Updated with the latest best practices.
Discover how to use Microsoft Teams Copilot to boost AI-powered productivity. Step-by-step guide, key features, and tips to transform meetings, chats, and tasks effortlessly. Unlock smarter collaboration today!
Tired of Microsoft Teams "Error D" files blocking your workflow? Get instant fixes for upload/download errors with this step-by-step troubleshooting guide. Resolve issues fast and boost productivity.
Tired of Microsoft Teams "Error Z" Zone crashing your meetings? Follow our expert, step-by-step guide to fix it quickly with the latest methods. Regain seamless teamwork now!
Tired of the frustrating Microsoft Teams "Check Version" error blocking your meetings? Follow our proven, step-by-step fixes to resolve it fast and restore smooth teamwork. Works on latest versions!
Struggling with the wrong Microsoft Teams account on Windows 11? Discover simple, step-by-step instructions to remove and change your Microsoft Teams account effortlessly. Perfect for managing work and personal profiles!
Struggling with Microsoft Teams "Guide" Tutorial Error? Discover simple, step-by-step fixes to resolve it quickly. Clear cache, update, and more for seamless teamwork. Updated for latest versions!