SMALL COMPLETION - Big side small must worry?
Researchers believe that this condition is related to the health of the baby later, including cancer and infertility.
Parents, while happily welcoming their son, you can leave out a little detail. Have you noticed that one testicle of your baby is bigger than the other testicle? This is called the hidden testicles (small and large testicles) and should be checked early. And what's more, there is research that shows a correlation between the hidden testicles in boys and their later health status.
But first ...
Big and small testicles: What are hidden testicles?
The hidden testicles (or testicles are small and large) is a fairly common phenomenon that occurs with 1: 100 boys. After giving birth, pregnant women may find that their son does not have one or both testicles inside the scrotum.
This strange situation occurs when the testicles do not develop on the outside. Instead, it develops in the abdomen while the baby is still in the womb. Hidden testicles happen when the testicles do not move away from the body in the right place - boys have only one or no testicles.
About 50% of boys infected will have testicles "move down" into the scrotum. The rest of the babies will probably be a few months later. With testicular failure, children may face other serious risks as they grow up.
Now, a new study by researchers at the University of Sydney warns that delaying surgery could put boys at risk of serious adult health problems.
Consequences if not treated for the hidden testicles
Recently, researchers from the University of Sydney have conducted a study on the hidden testicles (testicles are small and large) in boys.
After analyzing data on more than 350,000 boys born between 1970 and 1999, they discovered some shocking information. For boys with hidden testicles:
The chance of getting testicular cancer is 2.5 times higher
Fertility reduced by 20%
Needs double support for normal people when treating infertility
What is the reason for this phenomenon? Yes, for sperm production the testicle temperature needs to be lower than body temperature. This is exactly why the testicles have to “hang out” on the outside.
However, even though boys have hidden testicles, they are still inside the body. Current theories suggest that since these testicles are the same as body temperature, sperm cells will experience genetic problems and higher cell damage.
Over time, these conditions can accumulate as causing testicular cancer and other infertility problems.

SMALL COMPLETION - Big side small must worry?
When does my son need treatment?
It is always recommended that doctors perform testicular immobilization surgery when the baby is less than 18 months old.
Testicular immobilization surgery is a procedure where doctors remove the hidden testicles securely in the scrotum.
Researchers have found, though, that many actual surgeries do not take place during this time.
Professor Natasha Nassar is a long-time researcher on the above problem. "45 percent of boys still have surgery after 18 months of age," she said. I think maybe the problem is that people don't care about it, can't even open the diaper to check it out.
Other doctors feel more reassured when this surgery is done as soon as possible. For example, pediatric surgeon Professor Andrew Holland selects babies aged six months for this procedure.
Small lateral enlarged testicles in boys: Difficult to diagnose
In fact, it is very difficult to detect if your son has a hidden testicle (the testicle is big and small).
Babies need to be checked periodically (including the first 24 hours after birth). However, Professor Holland admits that certain skills are also needed to diagnose it.
One reason why it's so difficult to diagnose is that an infant's testicles are much smaller than those of an adult or a minor, according to Professor Holland.
"And I guess there was some confusion from parents or inspectors of this sensitive area that made them less enthusiastic about visiting," he said.
Sometimes there can also be other factors that are preventing a newborn's testicles from appearing. These factors also make it more difficult to diagnose the hidden testicles.
For example, sometimes sperm ropes (which connect to the testicles) develop at a rate slower than the body's growth rate. At that time, a spermatic rope will not be long enough to pull the testicles into the body.
Women who give birth earlier than expected should also be monitored. Preterm delivery can increase the risk of latent testicles in newborn boys, as they take longer to naturally move down.

Male genital problems are different than parents should exercise caution
Inguinal hernia
Occurs when the baby's abdominal tissue - for example the loops - moves into the baby's open groin canal. The main symptom of this disease is a small, painless blister in the baby's groin area. These hernias are more common in men than in women.
Treatment:
To prevent a blocked herniation, "a condition that occurs when a piece of intestine gets stuck and cuts off blood supply to that part of the intestine," a doctor may perform a small surgery to close the groin canal.
What if there is a stuffy hernia? The baby's groin area will be a hard, swollen and very painful lump that needs immediate medical treatment.
"When a boy's groin does not close, fluid from his abdomen can build up in the scrotum," said Dr. Steven Tennenbaum, a New York pediatric urologist. It causes the baby's testicles to swell, but not pain.
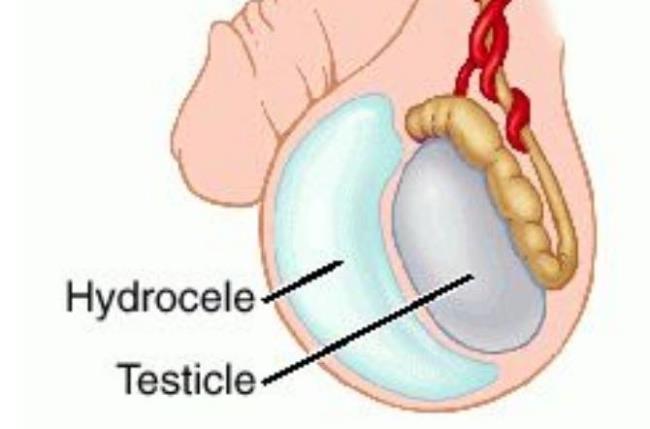
Treatment:
Hydroceles usually go away on their own. In the opposite case, the doctor may recommend surgery after your child's first birthday to remove the fluid and close the drain.
Urinary tract infection (UTI)
UTIs happen if a baby's penis is not cleaned properly. Bacteria thrive in this area. Usually, the only symptom of a urinary tract infection in a newborn is a high fever.
Or sometimes you notice that your baby's urine smells strange, he gets unusually angry or even vomiting. If you notice any of these symptoms, please consult your child's pediatrician early.
Treatment:
A course of antibiotics will easily treat t UTIs, according to doctors.
Risk of penis sticking
This can happen after circumcision. When body tissue is cut, edges can stick to the area around the cut. The scratch of the foreskin may stick to the foreskin, or other end.
If this happens, the penis will look like it has never been circumcised, or the foreskin is covered with a thin film.
Treatment:
The stickiness of the penis will not be painful and will most likely correct itself as the penis grows. There will be no need for treatment. However, if the adhesion is extended, a mild steroid cream may be prescribed to the patient, says Dr. Victoria McEvoy, assistant professor of pediatrics at Harvard Medical School.
Read more: Do babies need daily baths?