A child's foreskin stenosis is a condition in which the foreskin is too tight to pull over the tip of the penis. Foreskin stenosis is quite common and is normal in babies and toddlers, but in older children it can be the result of a skin condition that has caused scarring. It is usually not a problem unless it causes symptoms.
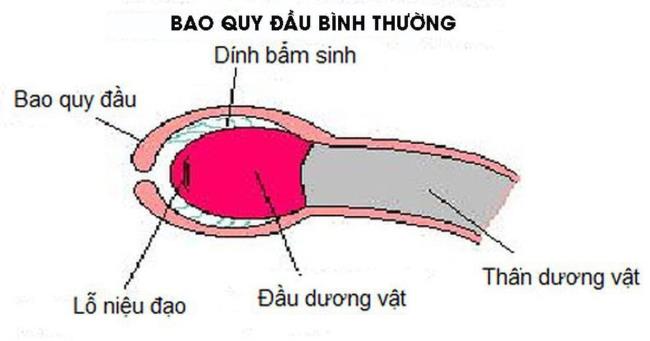
Foreskin (BQD) is the skin and mucous membrane covering the foreskin, which protects the foreskin from trauma and external bacteria enter the urethra, creating moisture for the foreskin.
Immediate treatment is required in the event of an infection causing problems such as difficulty urinating.
In order to recognize the child's stenosis, parents can observe that BQD holds the whole urinary hole, obstructing the flow of urine, when the child has a bulging foreskin, the urine is pulled back inside the foreskin. It often causes inflammation and itching. White particles inside the foreskin, also known as smegma residue, are accumulated by unhygienic mucosal secretions.
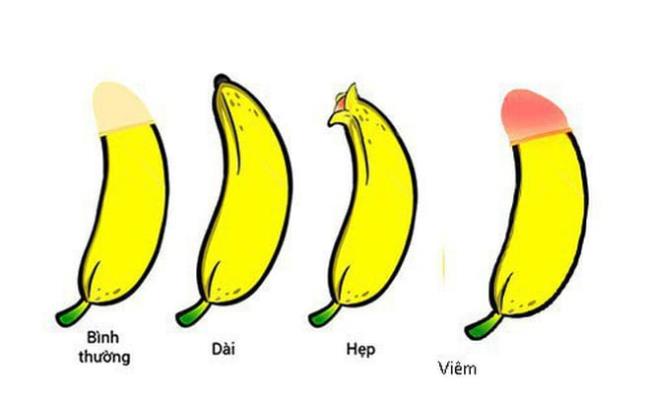
Foreskin stenosis in children
In children with long BQD, excess BQD in front of the foreskin, hindering flipping and hygiene.
Normal development
Most uncircumcised boys have foreskin that does not retract because it is still attached to the penis.
Foreskin stenosis in children
This is normal for the first 2 to 6 years. By about 2 years of age, the foreskin will begin to naturally separate from the foreskin.
Some boys' foreskin may take longer to separate, but this doesn't mean there's a problem - it will split at a later stage.
Never try to double your child's foreskin or try to extend it before it's ready as it can hurt and damage the foreskin.
When foreskin stenosis is an issue
BQD is not usually a very serious problem, unless it causes symptoms such as redness, pain, or swelling.
If they are painful and inflamed, they may develop a head infection.

There may also be a thick discharge under the foreskin. If both foreskin and foreskin are inflamed, it is called balanoposth inflammation.
See a doctor if they have these types of symptoms. Your doctor will be able to recommend appropriate treatment.
Most cases of balanitis can be easily treated using a combination of good hygiene, applying creams or ointments, and avoiding penis irritants.
Balanoposth inflammation can also sometimes be treated by following simple hygiene measures , such as keeping the penis clean by frequent washing with water and mild soap or moisturizer.
Urine can irritate the foreskin if it is retained for a long time under the foreskin, so it is advisable to remove the foreskin to wash the foreskin.
If balanoposthh is caused by a fungal or bacterial infection, an antifungal cream or a course of antibiotics may be needed.
How to properly clean and flipped BQD for children
To prevent narrow BQD for children, parents can perform gentle hand stretching BQD towards the base of the penis, every day and gradually often do when the child is bathing in a tub of water or after bathing the child in bed on his back. .
Remember that cleaning must be done daily by gently turning and rinsing with clean water.
It is possible to use topical drugs containing bethamethasone applied to the skin and mucous membranes of BQD, massage for 1-2 minutes to allow the drug to soak. The drug works to soften and thin the BQD skin, making it easier to flipped.
Pediatric and Newborn surgeons also said that in some Western countries, cutting BQD is a custom, making it easier to clean, reducing the risk of penile cancer and reducing the masturbation habits of some bars. Narrow BQD year.
It is important to clean your baby's penis regularly to avoid developmental problems.